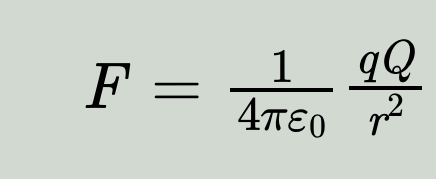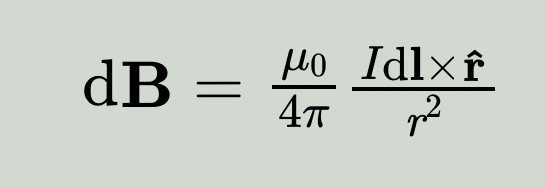Interactive timeline: To explore events click on circles.

1600 - De Magnete, Gilbert
Introduces the idea that the earth acts as a large bar magnet
Image credits: William Gilbert of Colchester, 'On the magnet, magnetick bodies also, and on the great magnet the earth a new physiology, demonstrated by many arguments & experiments', https://www.gutenberg.org/files/33810/33810-h/33810-h.html

1621 - Snell's law of diffraction
Willebrord Snellius (1580–1626)

1676 - Romer measures speed of light
Ole Christensen Rømer (1644-1710) used eclipses of Jupiter’s moons. c = 2.967 x 10^10 cm/s

1678 - Hygens puts forward his wave theory of light
Christiaan Huygen (1629-1695)

1704 - Newton - Opticks
Isaac Newton (1642-1727)

1752 - Franklin performs his electrical experiment with a kite in a thunderstorm
Benjamin Franklin (1705-1790). Modern alternative: https://www.lightningmaps.org/

1785 - Coulomb's law
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb (1736-1806) publishes his inverse square law of electrical attraction and repulsion.
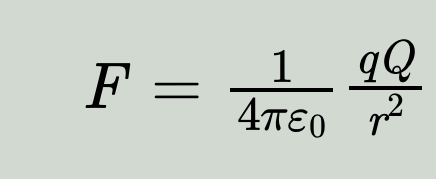
Image: Coulomb's torsion balance

1800 - Volta invents the voltaic pile
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (1745-1827)
Image: Alessandro Volta demonstrating his battery's generation of electric current before Napoleon (seated) in Paris in 1801.

1803 - Young provides evidence for the wave nature of light by demonstrating interference
Thomas Young (1773–1829)
Image: Interference patter of sunlight

1820 - Oersted publishes his discovery of electromagnetism
Hans Christian Øersted (1777-1851)

1820 - Biot-Savart Law
Jean-Baptiste Biot (1774-1862) and Félix Savart (1791-1841)
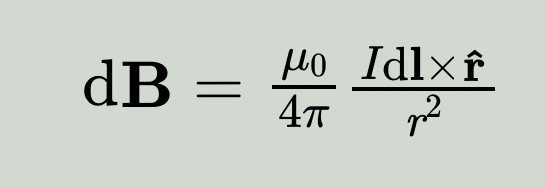

1813 - Brewster formulates a law for polarization by reflection (Brewster's law)
David Brewster (1781–1868)

1821 - Faraday constructs a simple electric motor
Michael Faraday (1791-1867)

1825 - Ampere deduces law for force between current-carrying conductors (Ampere's force law)
André-Marie Ampère (1775-1836)

1832 - Faraday performs experiments on electromagnetic induction, while Henry discovers self-induction
Michael Faraday (1791-1867), Joseph Henry (1797-1878)

1845 - Faraday discovers rotation of the plane of polarisation of the light when it propagates through material exposed to magnetic field
Michael Faraday (1791-1867)
Image credits: Faraday holding a piece of glass of the type he used to demonstrate the effect of magnetism on polarization of light, c. 1857.

1849 - Fizeau measures the speed of light by a toothed-wheel method
Armand Hippolyte Louis Fizeau (1819-1896)

1852 - Faraday's Lines of Magnetic Force
'A line of magnetic force may be defined as that line which is described by a very smail magnetic needle, wilen it is so moved in either direction correspondent to its length, that the needle is constantly a tangent to the line of motion; or it is that line along whictl, if a transverse wire be moved in either direction, there is no tendency to the formation of any current in the wire, whilst if moved in any other direction there is such a tendency; or it is that line which coincides with the direction of the magnecrystallic axis of a crystal of bismuth, which is carried in either direction along it. The direction of these lines about and amongst magnets and electric currents, is easily represented and understood. in a general manner, by the ordinary use of iron filing', Michael Faraday, 1852
Faraday, Michael. “On the Physical Character of the Lines of Magnetic Force,” Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, Fourth Series, 3, no. 20 (June 1852).
1864 - Dynamical Theory of Electric Field contains Maxwell's differential equations describing propagation of electromagnetic waves
James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879)

1888 - Hertz demonstrates propagation of electromagnetic waves (radio waves)
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857-1894)